       |
 The Human Breast The Human Breast
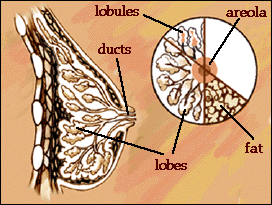
The main biological function of the female breast is to produce milk. Each of your breasts has 15 to 20 sections, called lobes, that are arranged in a flower shape like petals on a daisy. Lobes fill up with milk when a women is breast feeding.Each lobe has many smaller lobules which end in dozens of tiny bulbs which produce milk. The lobes, lobules, and bulbs are all linked by thin tubes called ducts. These ducts carry milk from the lobes to your nipple, located in the center of the dark area of skin on your breast called the areola. The spaces between the milk-producing parts of your breast are filled by fat. Muscles cover your ribs and lie under your breast, but they are not part of your breasts. |

